Elbow
Dislocation
- Home
- Conditions We Treat
- Elbow
- Elbow Dislocation

What is Elbow Dislocation?
The elbow joint is a hinge joint that connects the upper arm bone (humerus) to the forearm bones (radius, and ulna). It allows us to perform various movements like bending, straightening, and rotating the forearm. An elbow dislocation occurs when the bones that make up the elbow joint are forced out of their normal positions. This condition is usually caused by trauma or a fall, leading to severe pain, deformity, and inability to move the arm.
What are the types of Elbow Dislocation?
Classifying elbow dislocations is essential as it helps to ensure precise diagnosis. More importantly, it guarantees tailored-made treatments, focusing on the extent of bone displacement, and the associated damage to the joint, and surrounding tissues.
Based on Bone Displacement
- Complete dislocation (luxation) – complete dislocation often occurs when the bones in the elbow joints are fully separated, and pushed out of their normal alignment, leading to a complete loss of joint stability.
- Partial dislocation (subluxation) – partial dislocation happens when the bones in the joint are partially displaced but still maintain some level of contact. As a result, it causes significant discomfort, and instability.
Based on Tissue Damage
- Simple elbow dislocation – simple elbow dislocation involves ligament injuries that destabilise the joint but does not involve fractures to the bones forming the elbow.
- Complex elbow dislocation – complex elbow dislocation indicates severe injuries to ligaments, and tendons, often accompanied by fractures of the elbow bones.
- Severe elbow dislocation – severe elbow dislocation refers to damage to critical structures such as the blood vessels, and nerves surrounding the elbow, potentially compromising circulation, and nerve function.
What causes Elbow Dislocation?
The elbow is a joint where the bones, ligaments, and tendons come together to enable arm movement. However, a sudden force or trauma can disrupt this alignment, leading to dislocation. This can be caused by:
- Direct trauma – an example of direct trauma is falling onto an outstretched hand. It can also include high-impact injuries, such as those sustained in car accidents as they can force the bones in the elbow joint to be out of alignment.
- Sports injuries – activities involving intense arm movements, like gymnastics or contact sports, can exert excessive strain on the elbow joint.
- Weak ligaments – underlying conditions or prior injuries that weaken the ligaments may make the elbow more susceptible to dislocation.
What are the common symptoms?
Although the symptoms of elbow dislocation vary depending on the type, the common symptoms of elbow dislocation include:
- Severe pain in the elbow joint.
- Swelling, and bruising around the elbow.
- Tingling or numbness in the affected hand, wrist or forearm.
- Visible deformity or misalignment of the joint.
- Inability to bend or straighten the arm.
- Weaknesses in the affected arm.
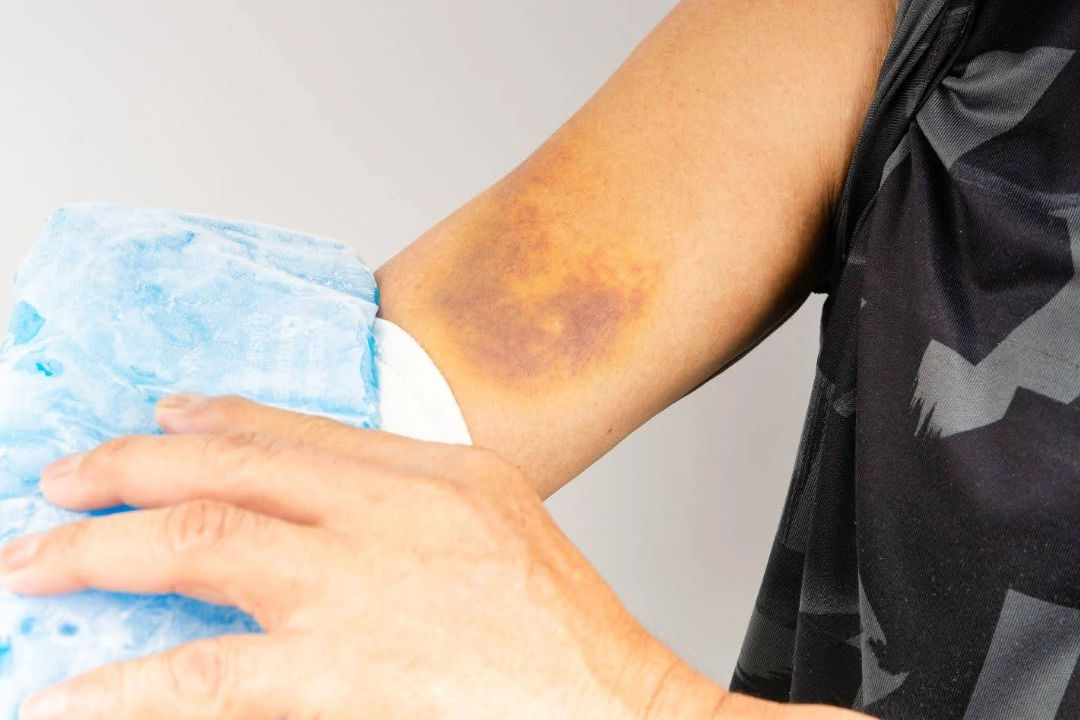
Who is at risk of Elbow Dislocation?
Elbow dislocation is relatively uncommon in Singapore. However, there are certain groups of people who are more susceptible to developing the condition. Some of the risk factors that increase the possibility of elbow include:
- Age – while elbow dislocation can affect people of all ages, it is more prevalent in young adults who engage in high-energy activities.
- Athletes – individuals participating in sports that require repetitive arm movements or involve high-impact falls, such as football or wrestling, are at greater risk.
- Children – due to their active lifestyle, and developing joints, children are more prone to experiencing partial dislocations, which is also called nursemaid’s elbow.
- Joint hypermobility – individuals with joint hypermobility are more prone to elbow dislocation as conditions like Ehlers-Danlos syndrome weakens the connective tissues.
- Occupational hazards – jobs requiring repetitive arm motions, such as construction work or heavy lifting, increase the likelihood of elbow injuries.
What are the complications of Elbow Dislocation?
Delaying treatment for elbow dislocation can lead to various complications that can impact your quality of life. This includes:
- Arthritis – over time, an improperly healed dislocation may contribute to the development of post-traumatic arthritis in the elbow joint.
- Blood vessel damage – severe dislocations can impair circulation in the arm, potentially causing serious complications if not addressed promptly.
- Chronic instability – damage to ligaments may cause recurrent dislocations or a feeling of looseness in the joint.
- Limited range of motion – scar tissue formation or joint damage can restrict movements, impacting daily activities.
- Nerve damage – the nerves surrounding the elbow can be compressed or torn, leading to numbness, tingling or weakness in the hand, and arm.
How is Elbow Dislocation diagnosed in Singapore?
Diagnosing elbow dislocation involves a detailed evaluation process to understand the severity, and nature of the condition. At Cove Orthopaedic Clinic, we begin by reviewing your medical history. Afterwards, the diagnostic process consists of:
Physical Examination
During a physical examination, our specialist will:
- Assess the appearance of the elbow joint for visible deformities.
- Check for swelling, and tenderness around the elbow.
- Examine the range of motion of the elbow.
- Evaluate for signs of blood vessel or nerve impairment.
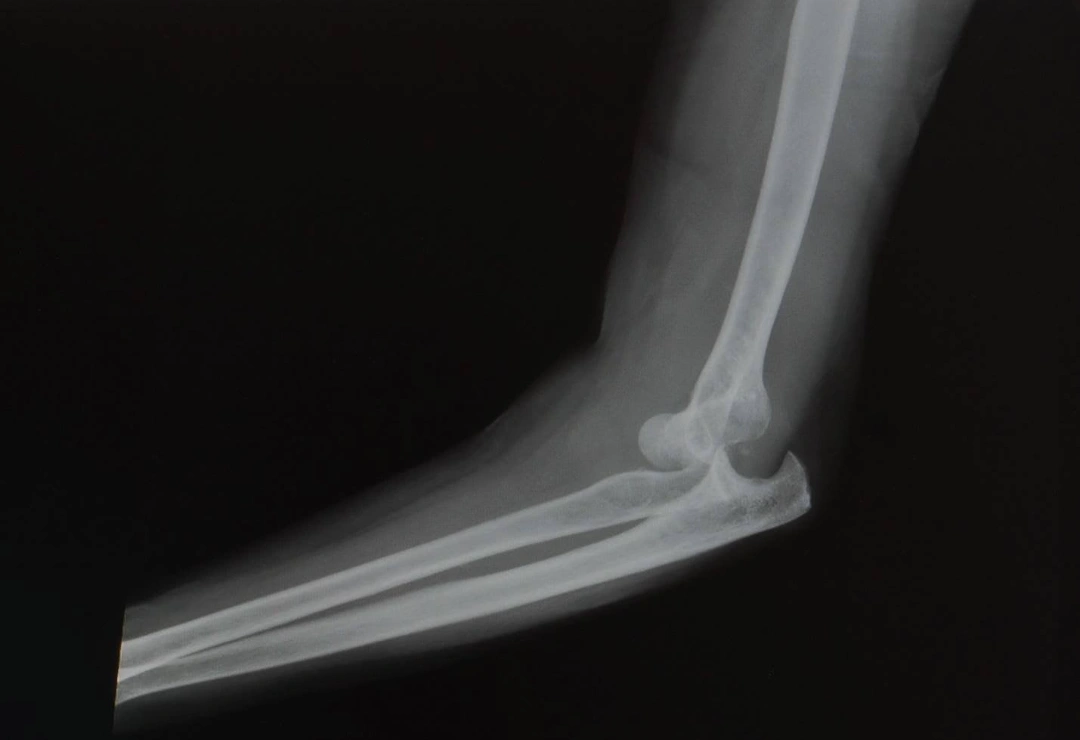
Imaging Tests
To obtain a comprehensive understanding of the condition, our specialist will order imaging tests to be done. This will include:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) – an MRI provides detailed images of the soft tissues, helping to identify ligament or tendon injuries.
- X-rays – an x-ray is often used to confirm the dislocation, and check for associated fractures, simultaneously ruling out elbow fracture as the cause behind the symptoms.
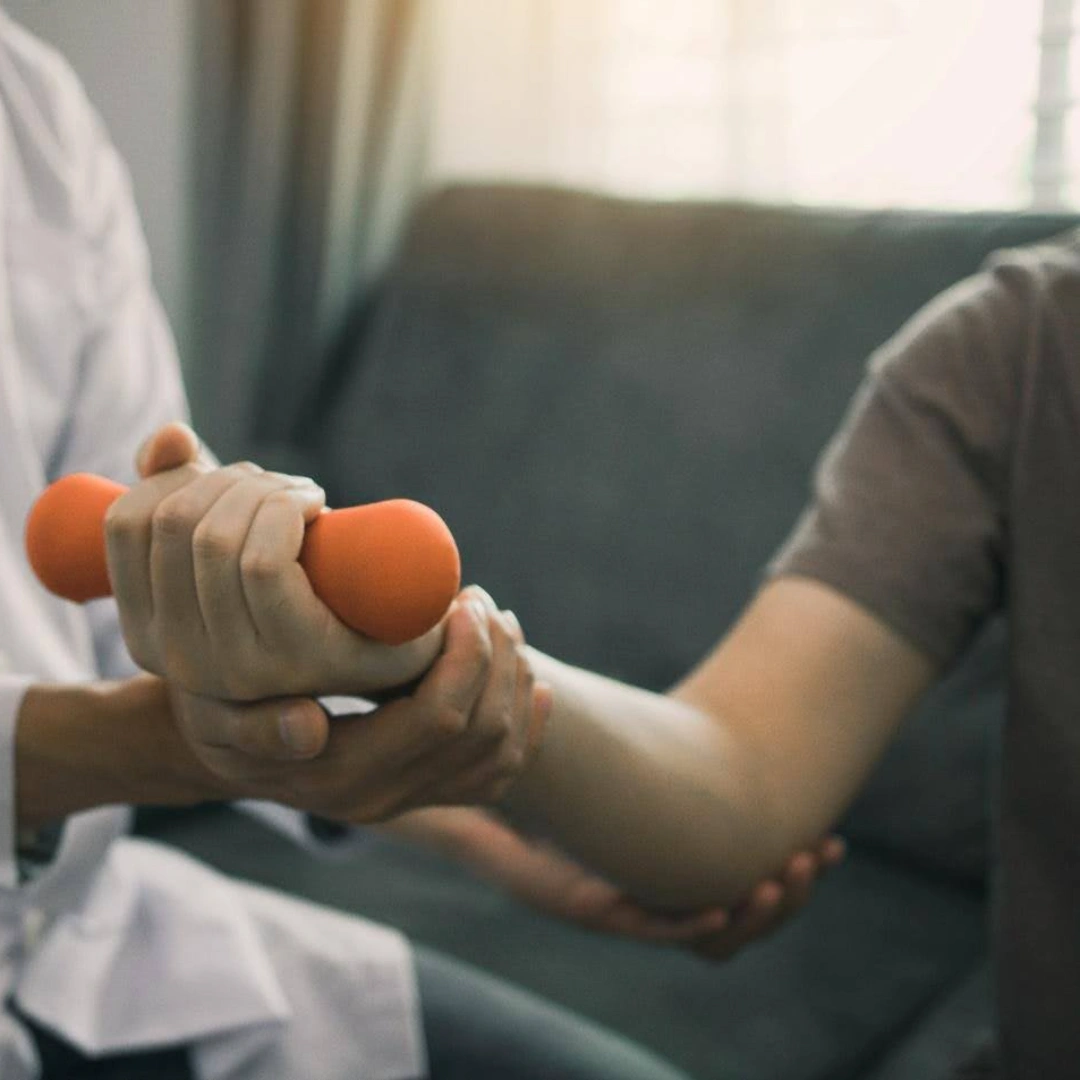

How is Elbow Dislocation treated in Singapore?
Once a conclusive diagnosis is confirmed, our orthopaedic specialist will outline a personalised treatment plan to help facilitate your recovery.
Conservative Treatments
Mild to moderate elbow dislocations can often be managed with conservative methods, including:
- Bracing, and immobilisation – a splint or sling may be used to stabilise the elbow, and allow the ligaments to heal.
- Medication – pain relievers, and anti-inflammatory drugs can alleviate discomfort, and reduce swelling.
- Reduction – reduction involves gently manoeuvring the bones back into their proper position.
Surgical Treatments
Meanwhile, severe or complex dislocations may require surgical intervention, such as:
- Fracture fixation – if the dislocation involves broken bones, fixation techniques such as screws, plates or rods are used to reconstruct the bone structure, and stabilise the joint.
- Joint reconstruction – in cases of extensive damage to the elbow structure, reconstruction may be required. This can include replacing or reshaping parts of the joint to restore alignment, and functionality, often in conjunction with soft tissue repairs.
- Ligament repair – the procedure involves repairing or reconstructing the torn ligaments that stabilise the elbow joint. However, our orthopaedic surgeons may use sutures or grafts to restore strength, and prevent recurring dislocations.
Rehabilitation Process
Rehabilitation is an essential part of recovery following surgical treatment. It ensures proper healing, prevents complications, and strengthens the joint to reduce the risk of future dislocations. Some of the key components that our orthopaedic specialist will focus on are:
- Gradual range of motion exercises – guided exercises are introduced early in the recovery process to reduce stiffness, improve flexibility, and maintain the elbow’s natural range of motion.
- Strength training – once healing progresses, targeted exercises focus on rebuilding strength in the muscles surrounding the elbow. This helps to provide better support, and stability to the joint.
- Return to activities – a phased approach allows patients to gradually resume daily activities, and sports. Additionally, special attention is given to avoid excessive strain on the joint during the recovery period.
Early diagnosis, and proper treatment are critical to restoring function, and preventing long-term complications. If you suspect elbow dislocation or are experiencing persistent elbow pain and immobility, schedule an appointment with us today for a detailed diagnosis and personalised treatment plan.
Conditions We Treat
Frequently asked questions
How painful is an elbow dislocation
Elbow dislocations are typically very painful due to the abrupt misalignment of bones, and potential damage to the surrounding ligaments, tendons or nerves. Patients have described the pain as immediate, and intense, often accompanied by swelling, and visible deformity.
Is it possible to dislocate both elbows?
Yes, it is possible. Although it is extremely rare, dislocating both elbows can happen during high-impact events such as falls or car accidents. This type of injury usually involves significant trauma, and requires urgent medical attention.
Will I still be able to move my arm with a dislocated elbow?
Movement is often severely limited or impossible with a dislocated elbow. Even if some movement is possible, attempting to move the joint can exacerbate the pain, and cause further damage to the surrounding tissues.
Can an elbow sprain lead to dislocated elbow?
Yes, and elbow sprain can lead to a dislocation, especially if the ligaments are weakened or severely injured. Ligaments play a key role in stabilising the joint, and significant damage may increase the risk of dislocation.
Why is it encouraged to see an orthopaedic specialist diagnose elbow dislocation?
An orthopaedic specialist can accurately diagnose the severity of an elbow dislocation, and rule out associated injuries such as fractures or nerve damage. They also ensure proper realignment, develop a personalised treatment plan, and guide rehabilitation to restore mobility, and prevent complications.
Can elbow dislocations be prevented?
While not all dislocations are preventable, you can reduce your risk by:
- Avoiding repetitive stress or overuse of the joint.
- Strengthening the muscles around the elbow to support joint stability.
- Using proper techniques during sports or physical activities.
- Wearing protective gear during high-risk activities.
How long does recovery usually take?
Recovery time for an elbow dislocation depends on the severity of the injury, and the treatment approach. But generally, the recovery time can take anywhere between three weeks to several months.
Will I regain full mobility post-recovery?
Yes, most patients regain functional use of the elbow, although some stiffness or reduced range of motion may persist. In such cases, you may require a longer timeline, and adjustments for ongoing care to ensure your elbow heals optimally, and fully.



