Chronic Ankle Instability
The ankle is one of the most commonly injured parts of the body in sports, with ankle sprain being the most common ankle injury. An ankle sprain occurs when there is injury to the ligaments that support the ankle, when they get stretched and torn due to a force that is beyond the normal range of motion, for example twisting the ankle.
It is important to seek treatment for an ankle sprain before returning to their regular activities, especially for people involved in sports. If not, this may lead to chronic ankle instability.
Chronic ankle instability refers to the recurrent ‘giving way’ of the outer (lateral) side of the ankle, which develops when ankle injuries do not heal properly, such as an ankle sprain.
1
Ankle sprains can be classified into 3 categories:
Grade 1
Mild ankle sprain with no significant tearing to the ligament
Grade 2
Moderate ankle sprain with a partial tear to the ligament
Grade 3
Severe ankle sprain with a complete tear to the ligament
Causes of ankle instability
Before you can look into ankle instability treatments, you must determine its root cause. Different causes of ankle instability may require different treatment approaches. Knowing the underlying cause helps your doctor recommend the right treatment to address the root issue.
Here are some of the most common causes of ankle instability.
Ankle sprains
A previous history of ankle sprains can weaken the ligaments, making the ankle more susceptible to instability.
Ligament damage
Direct damage to the ligaments can occur during traumatic injuries.
Muscle weakness
Muscle weakness around the ankle joint can lead to instability.
Abnormal anatomy
Some individuals may have anatomical variations that make them more prone to ankle instability.
What are the symptoms?
- Recurrent ankle sprains: Frequent “giving way” of the ankle, often resulting in recurrent sprains, which can be mild to severe.
- Pain: Pain around the ankle joint may be chronic or occur during and after physical activity.
- Swelling or inflammation: Ankle swelling, especially after an injury or physical activity.
- Weakness: A feeling of weakness in the ankle, which can affect the ability to stand or walk for extended periods.
- Loss of balance: Difficulty maintaining balance on one leg, leading to an increased risk of falls.
- Clicking or catching sensation: Some individuals may experience a clicking or catching sensation within the ankle joint.
- Difficulty in physical activities: Difficulty participating in sports that require running, jumping, or quick changes in direction.

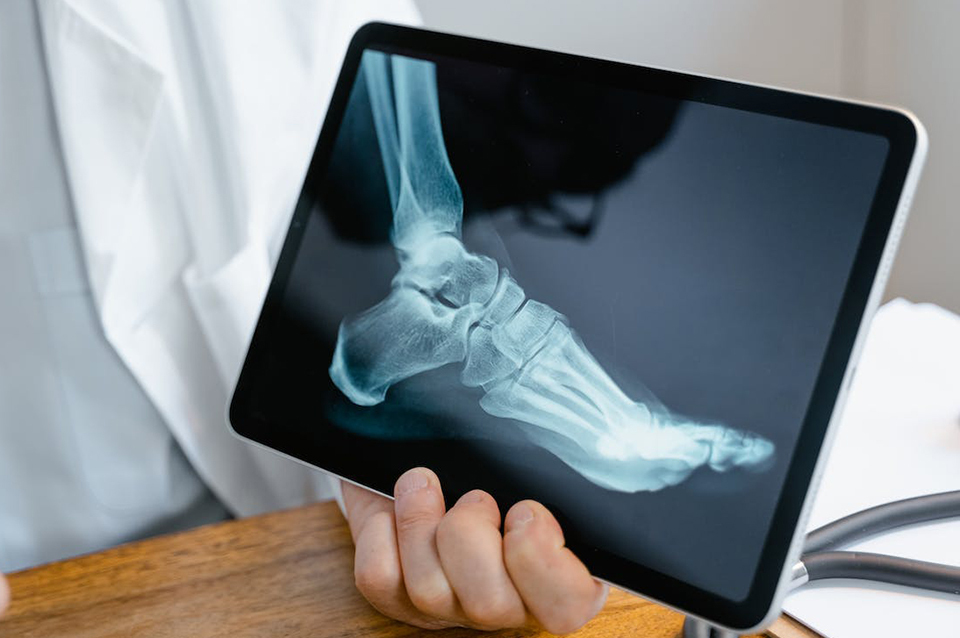
What is the diagnosis?
A history of the injury and a physical examination of the ankle will be conducted by the Doctor to check for tenderness and swelling of the ankle.
Imaging tests will be taken, such as a MRI scan where the doctor can check if there is any injury to the ligaments around the ankle.
What are the treatment options?
- Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen to relief pain and reduce inflammation
- Physiotherapy involving strengthening and balancing exercises to regain muscle strength and improve your balance
- Ankle guards to provide support to your ankle
- Exercises for weight loss, should there be a need for it
Should your ankle condition not improve after 3 months of nonsurgical methods such as physiotherapy, surgery may be recommended.
There are a few types of surgery, but the preferred one is minimally invasive surgery (MIS) using the Arthroscopic Broström-Gould Repair. Compared to open surgery, MIS uses smaller incisions, which result in lesser bleeding and a lower risk of wound complications.
What is the recovery process after surgery?
After the surgery, expect to wear a cast on your ankle which will immobilise it, promoting healing. Medications will be prescribed for pain relief as you may experience mild pain for a few days. After your stitches are removed, you will be wearing a walking boot and assigned simple ankle exercises to reduce the stiffness of your joints which will help to improve your range of motion.
Importance of rehabilitation in ankle instability
Ankle instability often results in weakened muscles, ligaments, and tendons around the ankle. Rehabilitation focuses on strengthening these structures, which is essential for restoring stability and functionality to the joint.
Reduced range of motion is also expected and is common due to pain and stiffness. Rehabilitation includes exercises and techniques to improve the ankle’s range of motion, allowing for a broader range of activities and reducing the risk of further injuries.
Ankle instability treatment in Singapore
There are many treatments that can address ankle instability. However, the right one can only be determined once the root cause of the condition is defined. Our orthopaedic specialists can help find the cause and recommend a suitable treatment plan.
Cove Orthopaedic Clinic believes early intervention is best to prevent the condition from progressing. We provide various treatments for ankle instability and are committed to help you regain your freedom of movement.
Take the first step toward recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
Strengthening your ankles at home is possible with targeted exercises such as calf raises, ankle alphabet exercises, towel scrunches, and resistance band exercises.
Conditions We Treat