Elbow Bursitis
- Home
- Conditions We Treat
- Elbow
- Elbow Bursitis
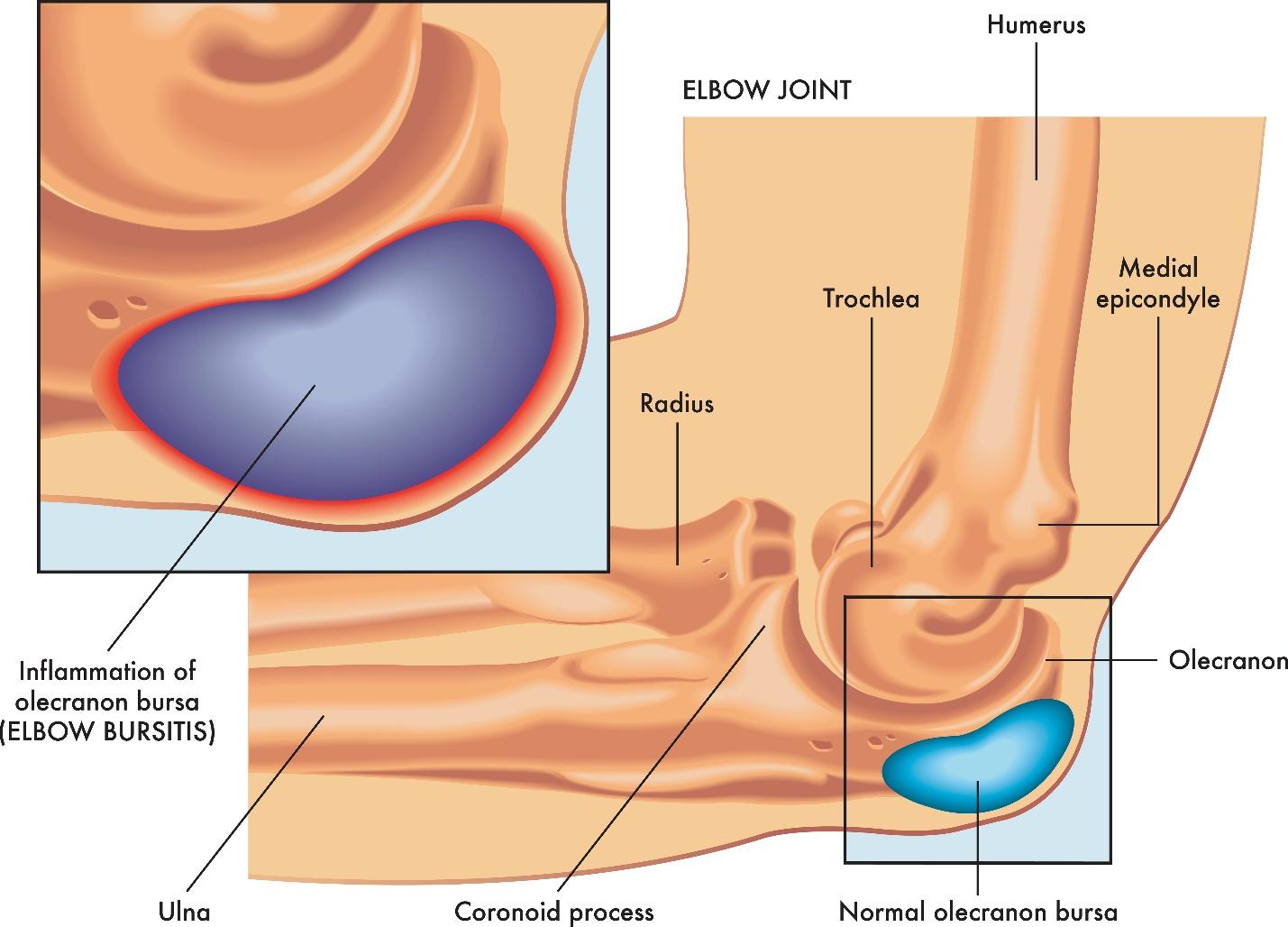
What is Elbow Bursitis?
Elbow bursitis occurs when the bursa, a fluid-filled sac near the elbow joint, becomes inflamed, and irritated. The bursa acts as a cushion, reducing friction between the skin, tendons, and bones. When the bursa becomes inflamed due to irritation or injury, it leads to swelling and discomfort. This condition may arise from repetitive movements, trauma or prolonged pressure on the elbow, causing it to become swollen, red, and painful.
What causes Elbow Bursitis?
The primary cause of elbow bursitis is repetitive friction or pressure on the elbow, which leads to irritation, and inflammation of the bursa. However, other contributing factors may include:
- Direct trauma or injury – a blow to the elbow, such as a fall or bump, can cause the bursa to become inflamed.
- Infection – an open wound on the elbow can allow bacteria to enter the bursa, leading to septic bursitis.
- Medical conditions – certain conditions such as gout or rheumatoid arthritis can make the bursa more susceptible to inflammation.
- Repetitive motions – frequent activities that involve leaning on the elbows or repetitive motions, like writing or certain sports, may irritate the bursa.
What are the symptoms of Elbow Bursitis?
Elbow bursitis presents a range of symptoms, which can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Some of the common symptoms include:
- Discolouration around the elbows
- Pain, especially when moving the elbows
- Painful when resting on elbows
- Redness, and warmth
- Reduced mobility
- Swelling around the elbows
Who is at risk of Elbow Bursitis?
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing elbow bursitis, especially in individuals with certain lifestyle factors or underlying health conditions. These may include:
- Athletes and manual workers – people who engage in repetitive activities, such as athletes or workers who frequently lean on their elbows, are at a higher risk.
- Gender – men are more susceptible to elbow bursitis due to the fact that more men are involved in manual labour work that involves repetitive movements compared to women.
- Older adults – age-related changes in the body can increase the likelihood of developing bursitis, especially those between 30 and 60 years old.
- Medical conditions – conditions like gout, rheumatoid arthritis or diabetes can contribute to the development of bursitis.
- Previous elbow injuries – a history of elbow trauma or fractures can predispose individuals to elbow bursitis.
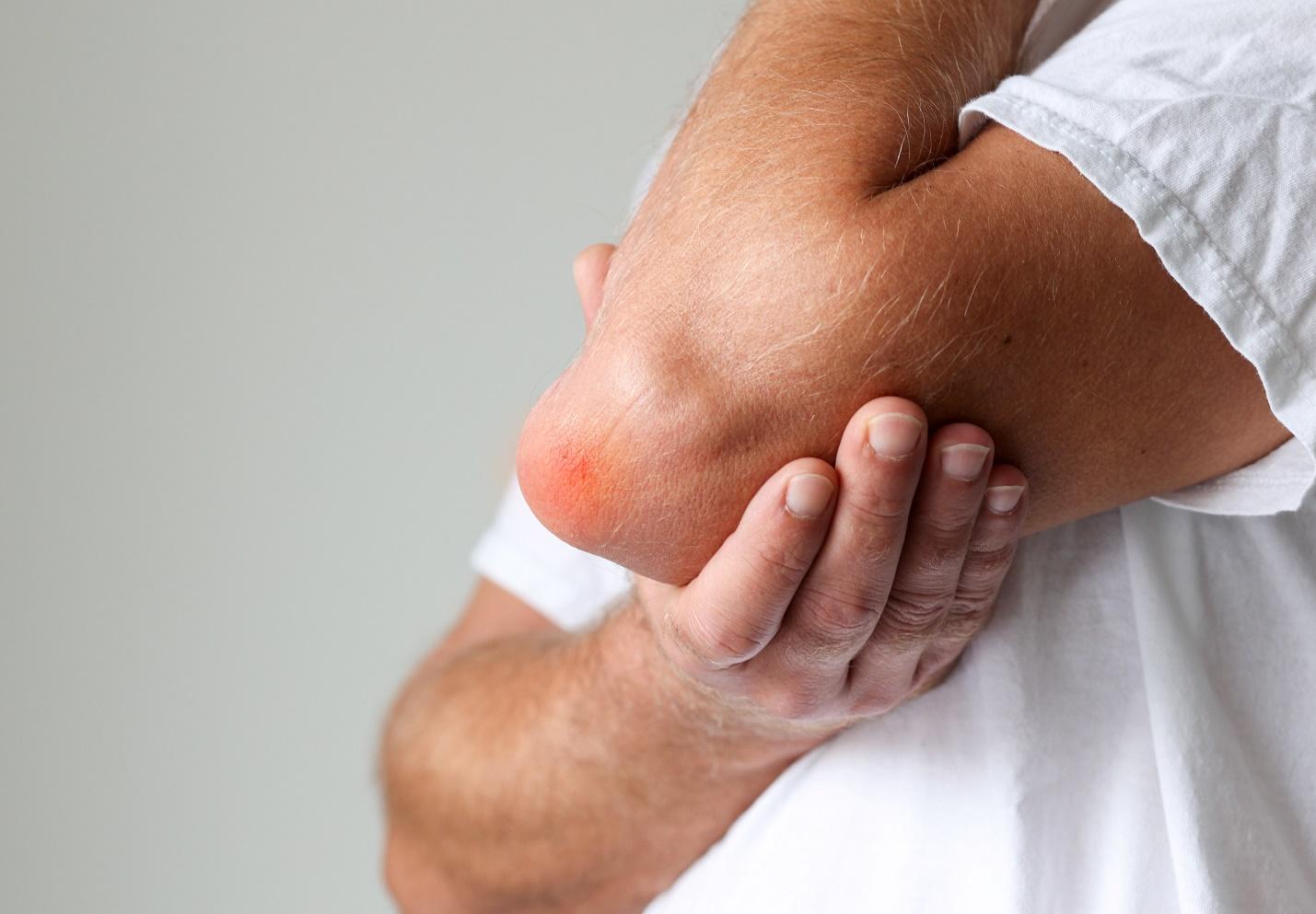
How does Elbow Bursitis impact quality of life?
Elbow bursitis can have a profound effect on an individual’s quality of life, particularly for those who rely on their elbows for daily activities. The inflammation, and swelling associated with this condition can significantly restrict movement, and cause discomfort, making even simple tasks challenging. For example, activities such as lifting objects, bending the arm or resting on the elbow can become painful or even impossible.
In a work setting, tasks that require repetitive use of the arms or prolonged sitting, such as typing, writing or operating machinery, may become difficult to perform. For those who enjoy sports or exercise, elbow bursitis can be particularly disruptive. The condition often limits participation in activities that involve arm movements, such as tennis, swimming or weightlifting, ultimately leading to reduced physical activity, and a sedentary lifestyle.
When left untreated or undiagnosed, elbow bursitis can lead to chronic pain, and long-term discomfort. This persistent pain can interfere with an individual’s ability to maintain an active lifestyle, impacting both personal, and professional aspects of life. In severe cases, the condition may result in deformity or permanent loss of movement in the elbow joint, further hindering everyday activities.
What is the difference between Elbow Bursitis, Tennis Elbow, and Elbow Cellulitis?
Elbow pain can stem from a variety of conditions, making it challenging to pinpoint the exact cause without professional evaluation. While elbow bursitis, tennis elbow, and elbow cellulitis share some similar symptoms, they each have distinct underlying causes, and risk factors.
| Condition | Elbow Bursitis | Tennis Elbow | Elbow Cellulitis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Causes | Inflammation of the bursa due to pressure or injury. | Overuse of tendons on the outside of the elbow. | Infection of the skin and soft tissues around the elbow. |
| Common Symptoms |
|
|
|
| Location | Back of the elbow. | Outer side of the elbow. | Skin around the elbow, often with visible redness. |
| Risk Factors |
|
|
|
| Treatment |
|
|
|
How is Elbow Bursitis diagnosed in Singapore?
We combine a thorough examination with diagnostic tests to accurately determine the cause of your elbow pain. This entails:
Initial Consultation
The diagnostic process begins with a comprehensive consultation to gather information about your medical history, and symptoms. This includes:
- Medical history – our specialists will review any past injuries, repetitive elbow use, underlying conditions such as arthritis or diabetes, and lifestyle or work habits that might contribute to elbow bursitis.
- Symptom inquiry – our specialist will ask you to describe the nature of your symptoms, including pain, swelling or tenderness, as well as their frequency and severity.
- Trigger identification – understanding whether certain activities, like prolonged leaning on the elbow or repetitive motions, trigger or worsen your symptoms helps us assess the severity of the condition.
Physical Examination
Once the initial consultation is complete, a thorough physical exam will follow. Our specialists will assess the extent of inflammation, and check for any signs of complications like infection. During this examination, our specialist will perform:
- Palpation – palpation involves gently pressing on the elbow to identify swelling or tenderness around the bursa.
- Range of motion check – this step enables our specialist to assess the elbow’s ability to move without pain or stiffness.
- Infection indicators – if signs of infection are present, such as redness, warmth or fever, our specialist will consider other conditions like elbow cellulitis.
Imaging Tests
Our specialist may recommend imaging tests to be performed to further assess your elbow, and rule out other possible conditions, such as fractures or arthritis. These tests may include:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) – an MRI is used to produce detailed views of the soft tissues in the elbow, specifically the muscles, and bursa. This helps the orthopaedic specialist to assess inflammation or potential structural problems.
- Ultrasound – an ultrasound provides a live image of the elbow, helping our specialists assess the size, and condition of the bursa, as well as any swelling or other abnormalities.
- X-rays – while X-rays do not capture soft tissues like the bursa, they are useful for identifying bone-related issues such as fractures or bone spurs that may contribute to elbow pain.
Aspiration and Laboratory Analysis
If there is a suspicion of infection or unusual swelling, our specialist may perform a procedure called aspiration. During this procedure, fluid is drawn from the swollen bursa, and sent for laboratory analysis to determine whether infection is present.
How is Elbow Bursitis treated in Singapore?
Treatment for elbow bursitis largely depends on the severity of symptoms. While conservative treatments are sufficient for many patients, our orthopaedic specialist may recommend surgery for persistent or severe cases.
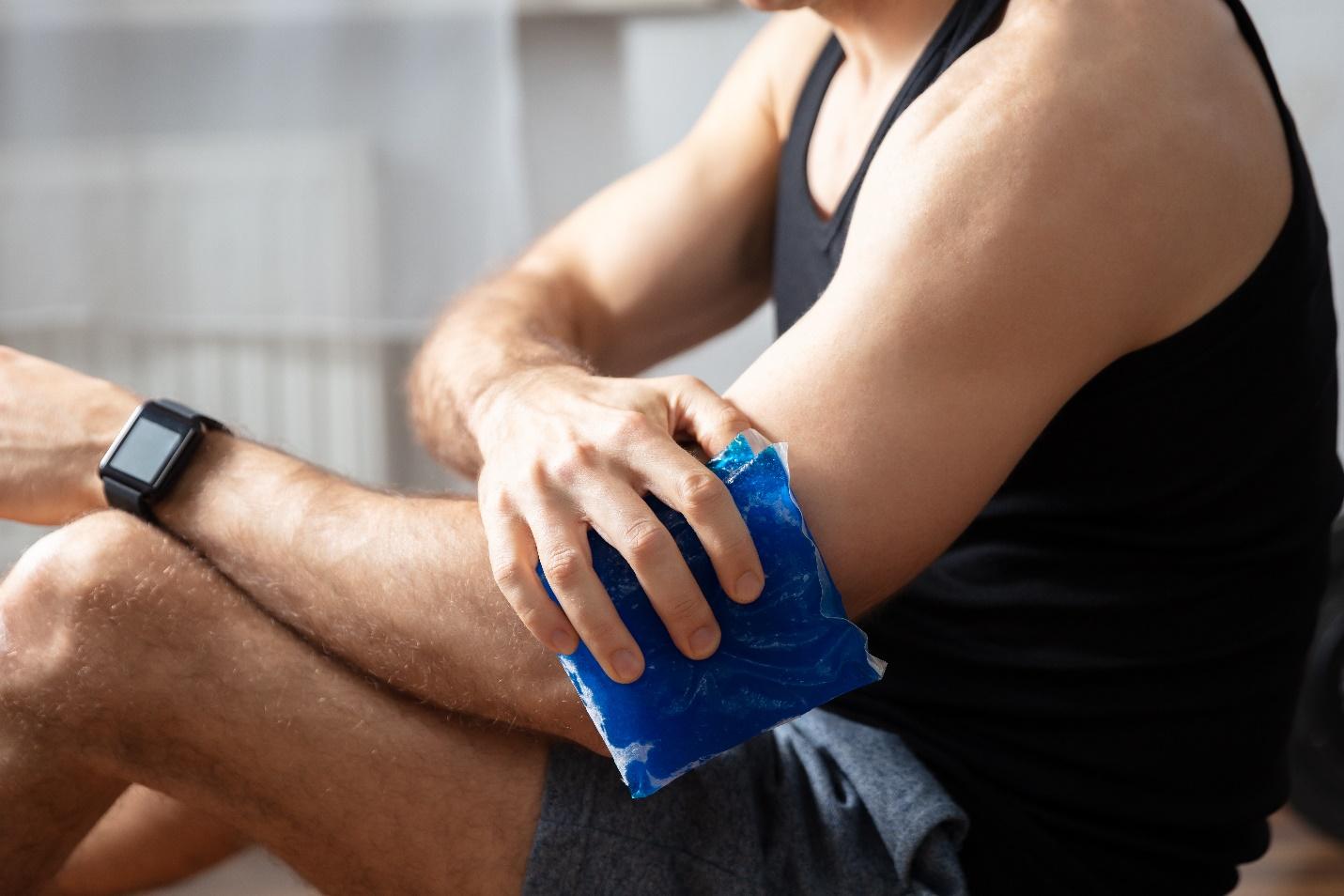

Conservative Treatments
- Anti-Inflammatory medication – non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), like ibuprofen, can help reduce pain, and swelling around the elbow.
- Rest and activity modification – avoiding activities that place strain on the elbow, such as leaning on it for extended periods or repetitive motions, can help reduce inflammation.
- Ice application – regular ice therapy can alleviate pain, and reduce swelling.
- Supportive bracing – wearing an elbow brace or sleeve provides additional support, and minimises unnecessary movement during the healing process.
- Physical therapy – targeted exercises designed to increase flexibility, strengthen muscles around the elbow, and prevent flare-ups can greatly benefit long-term recovery.
Injection Therapy
In cases where inflammation, and pain persist despite conservative treatments, corticosteroid injections may be recommended to provide targeted relief. These injections work by delivering powerful anti-inflammatory medication directly into the affected bursa, effectively reducing swelling, and discomfort.
While they can offer significant short-term relief, they are generally used with caution. This is because repeated or excessive use of corticosteroids can weaken surrounding tissues, potentially leading to further complications such as tendon weakening or joint instability.
Therefore, our specialists carefully assess each patient’s condition to determine whether an injection is appropriate, and ensure it is administered as part of a well-balanced treatment plan.
Surgical Options
- Bursal drainage or removal – if swelling persists despite conservative treatments, then our surgeon may proceed to drain the fluid from the bursa or remove the bursa entirely to prevent recurrence.
- Tissue decompression – tissue decompression relieves pressure on the bursa by removing any restrictive tissue or widening the space around the bursa.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
After treatment or surgery, a structured rehabilitation programme is essential to regain full function of the elbow:
- Gradual return to activity – once the initial inflammation subsides, patients can gradually return to normal activities, being mindful to avoid repetitive movements that may aggravate the condition.
- Physical therapy – a comprehensive therapy programme focusing on strengthening, and flexibility will help restore full range of motion, and prevent future issues.
Conclusion
Elbow bursitis, while often treatable with conservative methods, can cause significant discomfort, and impact daily life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effectively managing the condition.
If you are experiencing persistent pain or swelling in your elbow, seeking professional medical advice at an early stage will help ensure a faster recovery and prevent complications. Schedule a consultation with us today and start your journey towards pain relief and recovery.
Conditions We Treat
Frequently asked questions
What happens if elbow bursitis is left untreated?
Delaying treatment for elbow bursitis can lead to worsening symptoms, and potential complications. Persistent inflammation may cause chronic swelling, increasing the risk of long-term joint stiffness, and reduced mobility.
In cases of infected bursitis, postponing medical care can result in the spread of infection, requiring antibiotic treatment or even surgical drainage. Recurrent flare-ups can also weaken the bursa, and surrounding structures, making future episodes more severe, and difficult to manage.
Can elbow bursitis heal on its own?
In mild cases, elbow bursitis may resolve on its own with rest, and proper self-care. Additionally, reducing activities that put pressure on the elbow, applying ice packs, and using compression can help manage inflammation, and encourage healing.
However, if symptoms persist, worsen or involve signs of infection, such as warmth, redness or pus, medical intervention is necessary to prevent complications. As such, consulting an orthopaedic specialist ensures appropriate treatment for a full recovery.
How long does it take to recover from elbow bursitis?
Recovery time for elbow bursitis varies depending on its severity, and the chosen treatment approach.
- Mild cases – mild cases often improve within a few weeks with rest, ice therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications.
- Moderate cases – moderate cases may take several weeks to fully heal, especially if physical therapy is needed. If an infection is present, recovery may take longer due to the need for antibiotics or drainage.
- Severe cases – in cases requiring surgery, rehabilitation can extend recovery time to a few months.
Be that as it may, following a structured treatment plan can help speed up healing, and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Can elbow bursitis be prevented?
While elbow bursitis cannot always be prevented, the risk can be minimised by:
- Avoiding prolonged pressure
- Incorporating stretching routines
- Maintaining proper posture
- Making ergonomic adjustments
- Reducing repetitive stress
- Strengthening surrounding muscles
- Using protective padding
Which exercises should I avoid if I have elbow bursitis?
If you have elbow bursitis, it is important to avoid activities that exacerbate inflammation, and strain the joint. Exercises that place excessive pressure on the elbows, such as push-ups, planks, and heavy weightlifting, should be limited. Movements involving repetitive elbow bending, forceful gripping or direct impact to the elbow should also be approached with caution. Instead, focus on gentle stretching and mobility exercises that promote healing without aggravating the condition.
If you have been diagnosed with elbow bursitis, it is best to consult with an orthopaedic specialist to help tailor a safe and effective exercise routine.
Can massage therapy help relieve elbow bursitis pain?
Massage therapy may help alleviate elbow pain by improving circulation, and reducing muscle tension around the affected area. However, direct pressure on the inflamed bursa should be avoided, as it can worsen irritation and prolong recovery. Instead, gentle soft tissue massage around the surrounding muscles can help ease stiffness, and promote relaxation.
Can elbow bursitis return after treatment?
Yes, elbow bursitis can recur, especially if the underlying causes are not addressed. Additionally, repetitive stress, prolonged pressure on the elbow or improper ergonomics can contribute to future flare-ups.
To reduce the risk of recurrence, it is important to follow preventive strategies, such as modifying activities, using protective gear, and maintaining good joint health. Beyond that, strengthening the muscles around the elbow, and adopting proper movement techniques can also help prevent repeated episodes. If bursitis becomes a recurring issue, seeking medical advice can help identify, and manage contributing factors effectively.



